
2 months ago
Field research methods in social sciences
Causey, A. (2016). Drawn to See: Drawing as an Ethnographic Method, Toronto: University of Toronto Press.
Sanjek, R. (1990). Fieldnotes: The Makings of Anthropology. Ithaca: Cornell University press.
Weiss, R.S. (1995). Learning From Strangers: The Art and Method of Qualitative Interview Studies. Simon & Schuster.
Field research methods in design/UX
Dourish, P. (2006). Implications for design, in Proceedings of the conference on Human Factors in computing systems (Montréal, Québec),pp. 541–550, ACM.
Gaver, B., Dunne, T., & Pacenti E. (1999). Cultural Probes. Interactions, 6 (1), 21-29.
Gaver, W. W., Boucher, A., Pennington, S., & Walker, B. (2004). Cultural probes and the value of uncertainty. Interactions, 11 (5), 53-56. Retrieved from http://cms.gold.ac.uk/media/30gaver-etal.probes+uncertainty.interactions04.pdf
Goodman, E., Kuniavsky, M. & Moed, A.(2012). Observing the User Experience: A Practitioner’s Guide to User Research (2nd...

The history of design is really the history of materials. Dan Boyarski
1920: What should this look like?
1930: What should the form be?
1950: How can we design for production at scale?
1955: How should this work for people?
1960: How can organizations differentiate themselves?
1965: How should systems be structured?
1975: How should digital systems behave?
1990: What should the experience be?
1995: What should be designed?
2000: How might we affect human behavior?
2005: How should the service work?
2010: How should organizations be structured?
2015: How should societies behave?
2020: How should artificial intelligences behave?


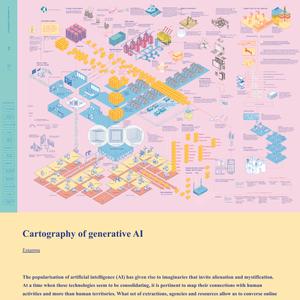

The theory of planned behaviour predicts that behaviour is preceded by the attitude towards the behaviour (i.e., beliefs and evaluation of the outcomes), subjective norms (i.e., the perception of the behaviour by others) and perceived behaviour control